部署 Ray Serve 应用
Contents
部署 Ray Serve 应用#
先决条件#
本指南仅重点介绍 Ray Serve 多应用程序 API,该 API 从 Ray 版本 2.4.0 开始提供。
Ray 2.4.0 或更高版本。
KubeRay 0.6.0、KubeRay nightly 或更高版本。
什么是 RayService?#
RayService 管理这些组件:
RayCluster: 管理 Kubernetes 集群中的资源。
Ray Serve 应用程序: 管理用户的应用程序。
RayService 提供什么?#
对 Ray 集群和 Ray Serve 应用程序的 Kubernetes 原生支持: 使用 Kubernetes 配置定义 Ray 集群及其 Ray Serve 应用程序后,您可以用
kubectl创建集群及其应用程序。Ray Serve 应用程序就地更新 用户可以更新 RayService CR 配置中的 Ray Serve 配置并使用
kubectl apply步骤 7 。Zero downtime upgrades for Ray clusters: 用户可以在RayService CR配置中更新Ray集群配置并用
kubectl apply更新集群。RayService 临时创建一个待处理集群并等待其准备就绪,然后将流量切换到新集群并终止旧集群。有关详细信息,请参阅 步骤 8 。Services HA: RayService监控Ray集群和Serve部署的健康状态。如果RayService在一段时间内检测到不健康状态,RayService会尝试创建新的Ray集群,并在新集群准备就绪时将流量切换到新集群。
示例:使用 RayService 为两个简单的 Ray Serve 应用程序提供服务
Step 1: 使用 Kind 创建 Kubernetes 集群#
kind create cluster --image=kindest/node:v1.23.0
Step 2: 安装 KubeRay operator#
按照 本文档 通过 Helm 存储库安装最新的稳定 KubeRay Operator。
请注意,本示例中的 YAML 文件使用 serveConfigV2 指定多应用程序 Serve 配置,从 KubeRay v0.6.0 开始支持该配置。
Step 3: 安装 RayService#
# Step 3.1: Download `ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml`
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ray-project/kuberay/v1.0.0-rc.0/ray-operator/config/samples/ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml
# Step 3.2: Create a RayService
kubectl apply -f ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml
首先查看RayService YAML 中嵌入的Ray Serve 配置 (即
serveConfigV2)。 请注意两个高级应用程序: 水果摊应用程序和计算器应用程序。请注意有关水果摊应用的一些细节:水果摊应用程序包含在 test_dag 中
fruit.py脚本的deployment_graph变量中,所以配置import_path指向此变量以告诉 Serve 从何处导入应用程序。水果应用程序托管在路由前缀
/fruit,这意味着以该前缀/fruit开头的路由的 HTTP 请求将发送到水果摊应用程序。工作目录指向 test_dag存储库,该存储库在运行时下载,RayService 在此目录中启动您的应用程序。 参阅 Runtime Environments 了解更多细节。
有关配置 Ray Serve 部署的更多详细信息,请参阅 Ray Serve 文档。
同样,计算器应用程序是从
conditional_dag.py导入的, 并且托管在路由前缀为/calc。
serveConfigV2: | applications: - name: fruit_app import_path: fruit.deployment_graph route_prefix: /fruit runtime_env: working_dir: "https://github.com/ray-project/test_dag/archive/41d09119cbdf8450599f993f51318e9e27c59098.zip" deployments: ... - name: math_app import_path: conditional_dag.serve_dag route_prefix: /calc runtime_env: working_dir: "https://github.com/ray-project/test_dag/archive/41d09119cbdf8450599f993f51318e9e27c59098.zip" deployments: ...
Step 4: 验证 Kubernetes 集群状态#
# Step 4.1: List all RayService custom resources in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get rayservice
# [Example output]
# NAME AGE
# rayservice-sample 2m42s
# Step 4.2: List all RayCluster custom resources in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get raycluster
# [Example output]
# NAME DESIRED WORKERS AVAILABLE WORKERS STATUS AGE
# rayservice-sample-raycluster-6mj28 1 1 ready 2m27s
# Step 4.3: List all Ray Pods in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get pods -l=ray.io/is-ray-node=yes
# [Example output]
# ervice-sample-raycluster-6mj28-worker-small-group-kg4v5 1/1 Running 0 3m52s
# rayservice-sample-raycluster-6mj28-head-x77h4 1/1 Running 0 3m52s
# Step 4.4: List services in the `default` namespace.
kubectl get services
# NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
# ...
# rayservice-sample-head-svc ClusterIP 10.96.34.90 <none> 10001/TCP,8265/TCP,52365/TCP,6379/TCP,8080/TCP,8000/TCP 4m58s
# rayservice-sample-raycluster-6mj28-head-svc ClusterIP 10.96.171.184 <none> 10001/TCP,8265/TCP,52365/TCP,6379/TCP,8080/TCP,8000/TCP 6m21s
# rayservice-sample-serve-svc ClusterIP 10.96.161.84 <none> 8000/TCP 4m58s
KubeRay 根据 RayService YAML 中定义的 spec.rayClusterConfig 创建 自定义资源 RayService 。
接下来,在 head Pod 运行并准备就绪后,KubeRay 向 head 的仪表板代理端口(默认:52365)提交请求,按照 spec.serveConfigV2 的定义创建 Ray Serve 应用程序。
当 Ray Serve 应用程序健康并准备就绪时,KubeRay 为 RayService 自定义资源创建一个头服务和一个服务服务(例如,在步骤 4.4 的 rayservice-sample-head-svc 和 rayservice-sample-serve-svc in Step 4.4)。
用户可以通过RayService管理的头服务(即 rayservice-sample-head-svc)和RayCluster管理的头服务(即rayservice-sample-raycluster-6mj28-head-svc)管理头服务。
但是,在零停机升级过程中,会创建一个新的 RayCluster,并为新的 RayCluster 创建一个新的头服务。
如果不使用 rayservice-sample-head-svc,则需要更新入口配置以指向新的头服务。
但是,如果您使用 rayservice-sample-head-svc,KubeRay 会自动更新选择器以指向新的 Head Pod,从而无需更新入口配置。
注意: 默认端口及其定义。
Port |
定义 |
|---|---|
6379 |
Ray GCS |
8265 |
Ray Dashboard |
10001 |
Ray Client |
8000 |
Ray Serve |
52365 |
Ray Dashboard Agent |
步骤 5: 验证服务应用程序的状态#
# Step 5.1: Check the status of the RayService.
kubectl describe rayservices rayservice-sample
# Active Service Status:
# Application Statuses:
# fruit_app:
# Health Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Serve Deployment Statuses:
# fruit_app_DAGDriver:
# Health Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Status: HEALTHY
# fruit_app_FruitMarket:
# ...
# Status: RUNNING
# math_app:
# Health Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Serve Deployment Statuses:
# math_app_Adder:
# Health Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Last Update Time: 2023-07-11T22:21:24Z
# Status: HEALTHY
# math_app_DAGDriver:
# ...
# Status: RUNNING
# Step 5.2: Check the Serve applications in the Ray dashboard.
# (1) Forward the dashboard port to localhost.
# (2) Check the Serve page in the Ray dashboard at http://localhost:8265/#/serve.
kubectl port-forward svc/rayservice-sample-head-svc --address 0.0.0.0 8265:8265
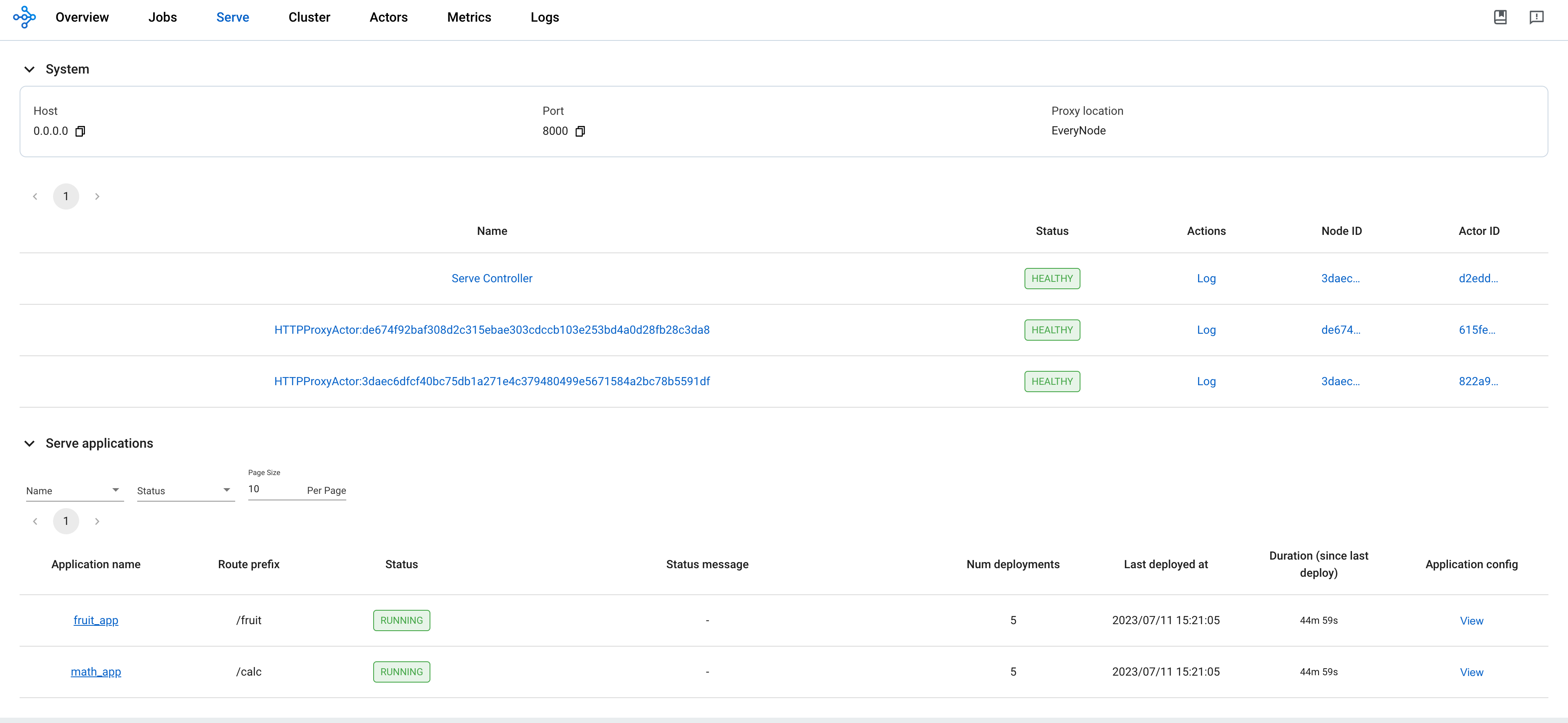
有关 RayService 可观测性的更多详细信息,请参阅 rayservice-troubleshooting.md 。 下面是 Ray 仪表板中服务页面的屏幕截图示例。
步骤 6: 通过 Kubernetes 服务向服务应用程序发送请求#
# Step 6.1: Run a curl Pod.
# If you already have a curl Pod, you can use `kubectl exec -it <curl-pod> -- sh` to access the Pod.
kubectl run curl --image=radial/busyboxplus:curl -i --tty
# Step 6.2: Send a request to the fruit stand app.
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' rayservice-sample-serve-svc:8000/fruit/ -d '["MANGO", 2]'
# [Expected output]: 6
# Step 6.3: Send a request to the calculator app.
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' rayservice-sample-serve-svc:8000/calc/ -d '["MUL", 3]'
# [Expected output]: "15 pizzas please!"
rayservice-sample-serve-svc一般是HA。 它在所有具有 Serve 部署的工作线程之间进行流量路由,并且始终尝试指向健康的集群,即使在升级或失败的情况下也是如此。
步骤 7: Ray Serve 应用程序就地更新#
您可以通过修改 RayService 配置文件的 serveConfigV2 来更新应用程序的配置。 使用 kubectl apply 重新应用修改后的配置会将新配置重新应用到现有 RayCluster,而不是创建新的 RayCluster。
将 ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml 中水果摊应用的芒果价格从 3 修改为 4 。 此更改重新配置了现有的 MangoStand 部署,未来的请求将使用更新后的 Mango 价格。
# 步骤 7.1: Update the price of mangos from 3 to 4.
# [ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml]
# - name: MangoStand
# num_replicas: 1
# user_config:
# price: 4
# 步骤 7.2: Apply the updated RayService config.
kubectl apply -f ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml
# 步骤 7.3: Check the status of the RayService.
kubectl describe rayservices rayservice-sample
# [Example output]
# Serve Deployment Statuses:
# - healthLastUpdateTime: "2023-07-11T23:50:13Z"
# lastUpdateTime: "2023-07-11T23:50:13Z"
# name: MangoStand
# status: UPDATING
# 步骤 7.4: Send a request to the fruit stand app again after the Serve deployment status changes from UPDATING to HEALTHY.
# (Execute the command in the curl Pod from 步骤 6)
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' rayservice-sample-serve-svc:8000/fruit/ -d '["MANGO", 2]'
# [Expected output]: 8
步骤 8: Ray 集群零停机升级#
在步骤 7, 修改 serveConfigV2 不会触发Ray集群的零停机升级。相反,它将新配置重新应用到现有 RayCluster。
但是,他将新的配置应用于已有的集群。
然而,如果你修改了 RayService YAML 配置文件的 spec.rayClusterConfig ,则会触发 Ray 集群的零停机升级。
RayService 临时创建一个新的 RayCluster 并等待其准备就绪,然后通过更新 RayService 管理的头服务的选择器(即 rayservice-sample-head-svc)将流量切换到新的 RayCluster 并终止旧的 RayCluster。
在零停机升级过程中,RayService会临时创建一个新的RayCluster并等待其准备就绪。
一旦新的RayCluster准备就绪,RayService会更新RayService管理的头部服务的选择器(即 rayservice-sample-head-svc),使其指向新的RayCluster,从而将流量切换到新的RayCluster。
最后,旧的 RayCluster 被终止。
某些异常不会触发零停机升级。
只有 Ray Autoscaler 管理的字段 replicas 和 scaleStrategy.workersToDelete 不会触发零停机升级。
当您更新这些字段时,KubeRay 不会将更新从 RayService 传播到 RayCluster 自定义资源,因此不会发生任何情况。
# 步骤 8.1: Update `spec.rayClusterConfig.workerGroupSpecs[0].replicas` in the RayService YAML file from 1 to 2.
# This field is an exception that doesn't trigger a zero downtime upgrade, and nothing happens.
kubectl apply -f ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml
# 步骤 8.2: Check RayService CR
kubectl describe rayservices rayservice-sample
# Worker Group Specs:
# ...
# Replicas: 2
# 步骤 8.3: Check RayCluster CR. The update doesn't propagate to the RayCluster CR.
kubectl describe rayclusters $YOUR_RAY_CLUSTER
# Worker Group Specs:
# ...
# Replicas: 1
# 步骤 8.4: Update `spec.rayClusterConfig.rayVersion` to `2.100.0`.
# This field determines the Autoscaler sidecar image, and triggers a zero downtime upgrade.
kubectl apply -f ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml
# 步骤 8.5: List all RayCluster custom resources in the `default` namespace.
# Note that the new RayCluster is created based on the updated RayService config to have 2 workers.
kubectl get raycluster
# NAME DESIRED WORKERS AVAILABLE WORKERS STATUS AGE
# rayservice-sample-raycluster-6mj28 1 1 ready 142m
# rayservice-sample-raycluster-sjj67 2 2 ready 44s
# 步骤 8.6: Wait for the old RayCluster terminate.
# 步骤 8.7: Submit a request to the fruit stand app via the same serve service.
curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' rayservice-sample-serve-svc:8000/fruit/ -d '["MANGO", 2]'
# [Expected output]: 8
触发新 RayCluster 准备的其他可能场景
Note: 以下行为适用于 KubeRay v0.6.2 或更高版本。 对于旧版本,请参阅 kuberay#1293 了解更多详细信息。
如果 KubeRay 认为 RayCluster 不健康,它也会触发新的 RayCluster 准备。 在 RayService 中,KubeRay 可以在两种可能的情况下将 RayCluster 标记为不健康。
情况 1: KubeRay operator 无法连接到 Head Pod 上的仪表板代理的时间超过
deploymentUnhealthySecondThreshold参数定义的持续时间。 默认值和示例 YAML 文件中deploymentUnhealthySecondThreshold的值均为 300 秒。情况 2: 如果服务应用的状态
DEPLOY_FAILED或UNHEALTHY的持续时间超过serviceUnhealthySecondThreshold参数,KubeRay operator 会将 RayCluster 标记为不健康。默认值和示例 YAML 文件中serviceUnhealthySecondThreshold的值均为 900 秒。
KubeRay 将 RayCluster 标记为不健康后,它会启动新 RayCluster 的创建。一旦新的 RayCluster 准备就绪,KubeRay 会将网络流量重定向到它,然后删除旧的 RayCluster。
步骤 9: 清理 Kubernetes 集群#
# 删除 RayService.
kubectl delete -f ray_v1alpha1_rayservice.yaml
# 卸载 KubeRay operator。
helm uninstall kuberay-operator
# 删除 curl Pod.
kubectl delete pod curl
下一步#
如果遇到任何问题,请参阅 RayService 故障排除指南 。
有关更多 RayService 示例,请参阅 Examples 。 MobileNet 示例 是一个很好的入门示例,因为它不需要 GPU 并且很容易在本地计算机上运行。