Seldon Core 批处理¶
Seldon Core 提供了一个命令行组件,允许使用水平可扩展的 Seldon 核心 kubernetes 模型部署进行高度并行化的批处理。
流处理请查看基于 KNative 事件的流处理。
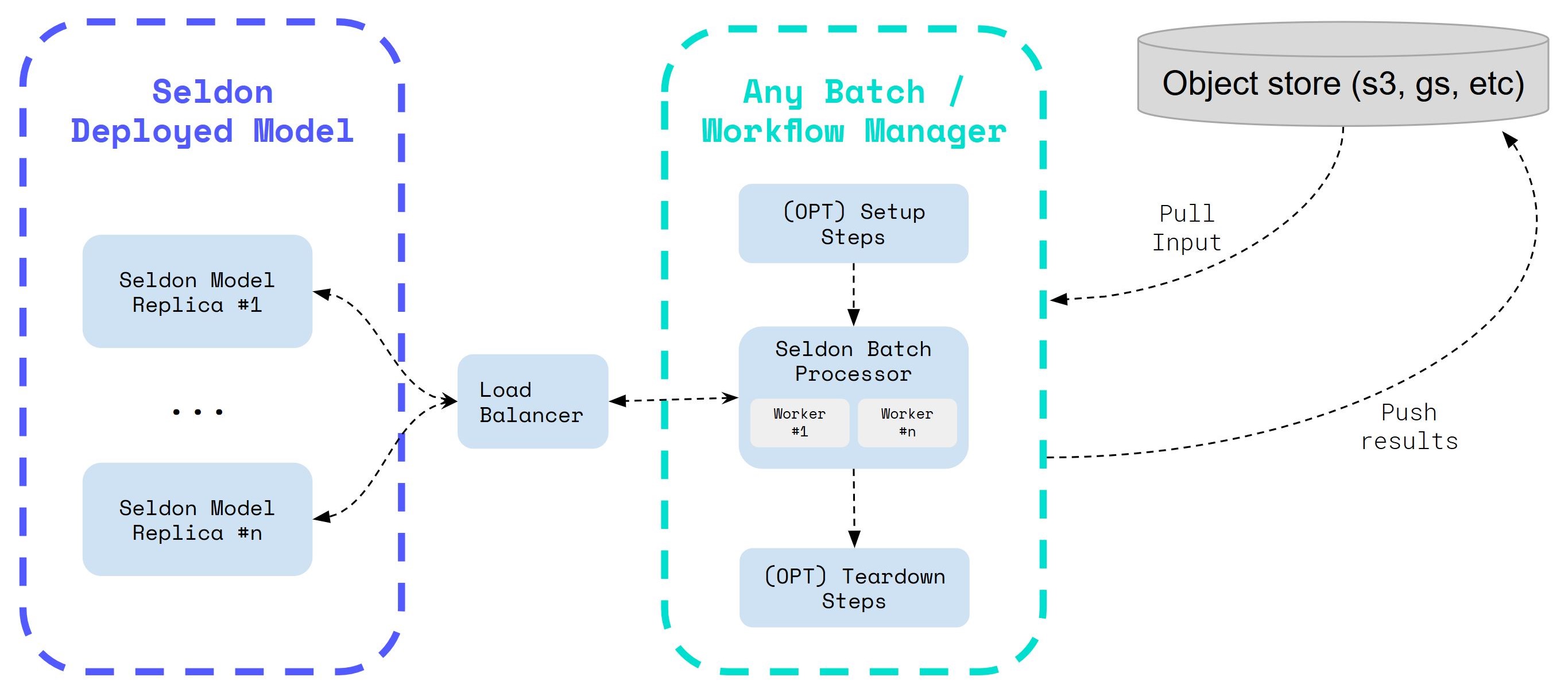
水平可扩展的 Workers 和副本¶
可并行化的批处理器工作线程允许高吞吐量,因为它能够利用 Seldon Core 水平扩展副本以及自动扩展,从而为用户提供灵活性以根据需要优化他们的配置。
下图显示了一个标准工作流程,其中可以下载数据然后通过对象存储上传,并且可以在作业成功完成后创建和删除 Seldon 模型。
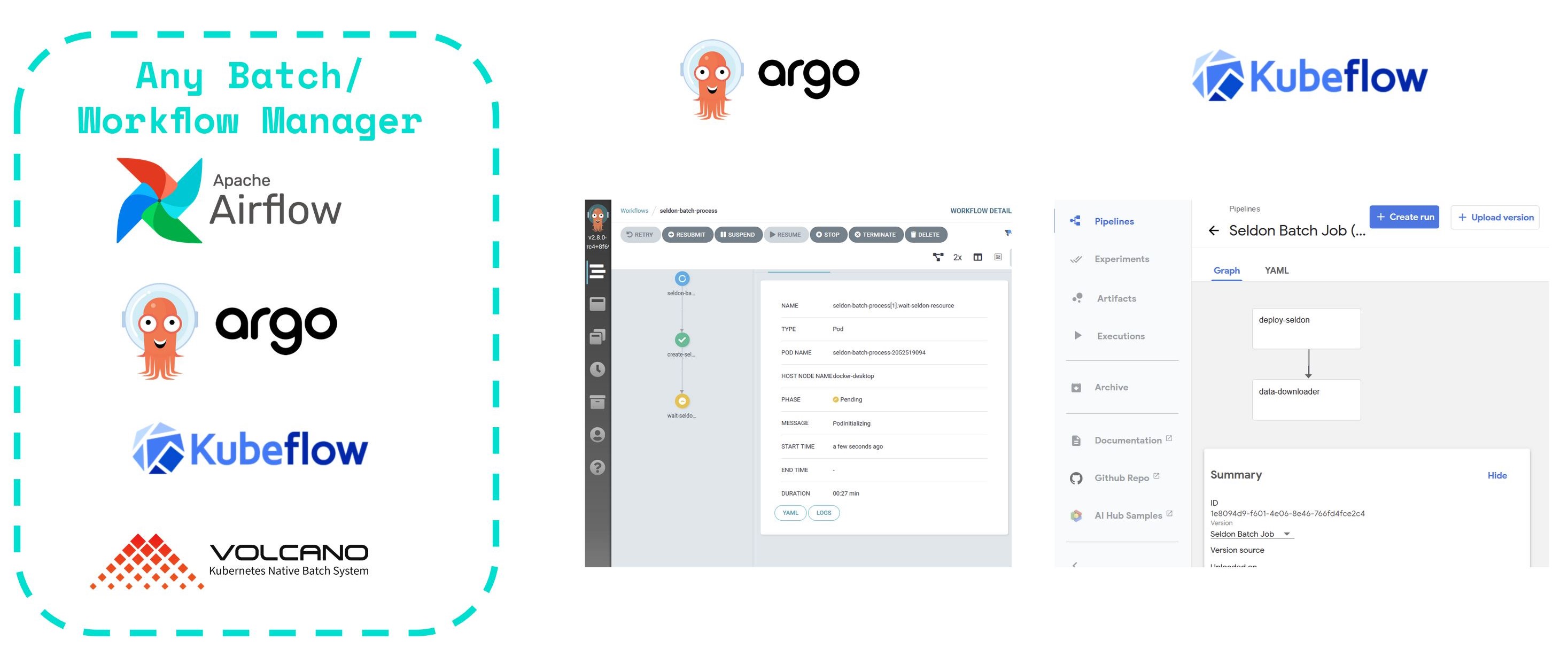
与 ETL 和工作流管理器集成¶
Seldon 批处理组件已构建为模块化和灵活化的,因此它可以跨任何工作流管理器进行集成。
这允许您在大量批处理应用程序上利用 Seldon,包括必须按计划发生的触发器(例如,每天一次、每月一次等),或可以以编程方式触发的作业。
动手实例¶
我们提供了一组示例,向您展示如何使用 Seldon 批处理组件:
高级实现细节¶
命令行参数¶
要获得有关每个可用命令的更多信息,您可以按如下方式与批处理器组件交互:
$ seldon-batch-processor --help
Usage: seldon-batch-processor [OPTIONS]
Command line interface for Seldon Batch Processor, which can be used to send
requests through configurable parallel workers to Seldon Core models. It is
recommended that the respective Seldon Core model is also optimized with
number of replicas to distribute and scale out the batch processing work.
The processor is able to process data from local filestore input file in
various formats supported by the SeldonClient module. It is also suggested
to use the batch processor component integrated with an ETL Workflow Manager
such as Kubeflow, Argo Pipelines, Airflow, etc. which would allow for extra
setup / teardown steps such as downloading the data from object store or
starting a seldon core model with replicas. See the Seldon Core examples
folder for implementations of this batch module with Seldon Core.
Options:
-d, --deployment-name TEXT The name of the SeldonDeployment to send the
requests to [required]
-g, --gateway-type [ambassador|istio|seldon]
The gateway type for the seldon model, which
can be through the ingress provider
(istio/ambassador) or directly through the
service (seldon)
-n, --namespace TEXT The Kubernetes namespace where the
SeldonDeployment is deployed in
-h, --host TEXT The hostname for the seldon model to send
the request to, which can be the ingress of
the Seldon model or the service itself
-t, --transport [rest|grpc] The transport type of the SeldonDeployment
model which can be REST or GRPC
-a, --data-type [data|json|str|raw]
Whether to use json, strData or Seldon Data
type for the payload to send to the
SeldonDeployment which aligns with the
SeldonClient format
-p, --payload-type [ndarray|tensor|tftensor]
The payload type expected by the
SeldonDeployment and hence the expected
format for the data in the input file which
can be an array
-w, --workers INTEGER The number of parallel request processor
workers to run for parallel processing
-r, --retries INTEGER The number of retries for each request
before marking an error
-i, --input-data-path PATH The local filestore path where the input
file with the data to process is located
-o, --output-data-path PATH The local filestore path where the output
file should be written with the outputs of
the batch processing
-m, --method [predict|feedback]
The method of the SeldonDeployment to send
the request to which currently only supports
the predict method
-l, --log-level [debug|info|warning|error]
The log level for the batch processor
-b, --benchmark If true the batch processor will print the
elapsed time taken to run the process
-u, --batch-id TEXT Unique batch ID to identify all data points
processed in this batch, if not provided is
auto generated
-s, --batch-size INTEGER Batch size greater than 1 can be used to
group multiple predictions into a single
request.
-t, --batch-interval FLOAT Minimum Time interval (in seconds) between
batch predictions made by every worker.
--use-ssl BOOLEAN Whether to use https rather than http as the
REST transport protocol.
--call-credentials-token TEXT Auth token used by Seldon Client, if
supplied and using REST the transport
protocol will be https.
--ssl-verify BOOLEAN Can be set to false to avoid SSL
verification in REST.
--help Show this message and exit.
身份标识¶
发送到 Seldon 核心模型的每个数据点在请求元数据中包含以下标识符:
Batch ID - 可以通过 CLI 提供或自动生成的唯一标识符
Batch Instance ID - 为每个处理的数据点生成的唯一标识符
Batch Index - 数据点相对于输入文件位置的本地有序降序索引
这些标识符按如下方式添加到每个请求中:
seldon_request = {
<data>: <current_batch_instance>,
"meta": {
"tags": {
"batch_id": <BATCH_ID>
"batch_instance_id": <BATCH_INSTANCE_ID>
"batch_index": <BATCH_INDEX>
}
}
}
这允许识别请求并将其与数据中的初始请求进行匹配。
表现¶
该模块的实现是利用 Python 的线程系统完成的。
基准测试是使用普通 Python 请求模块进行的,以评估 Threading、Twisted 和 AsyncIO 的性能。结果显示 Asyncio 的性能更好,但是考虑到工作程序中的逻辑非常少(即发送请求)并且大部分时间都在等待响应,使用 Python 的本机线程的实现能够以最快的速度执行足够高效,可以很容易地扩展到数千工作器。
然而,目前的实现使用 Seldon 客户端,它没有利用很多优化要求来提高处理性能,例如重用 requests.py 会话。然而,即使没有这些优化,worker 仍将达到高度并发的性能,并且这些优化将随着该组件(和反馈)的采用率的增长而引入。
微批量¶
使用批处理器 CLI 时,您可以指定一个 batch-size 参数,该参数可以将多个预测分组到单个请求中。这使您可以利用为某些模型提供的更高性能,并减少网络开销。响应将被拆分回多个单个预测响应,以便输出文件看起来与运行批处理大小为 1 的处理器相同。
目前我们只支持微批处理ndarray和tensor有效载荷类型。
输入文件格式¶
数据类型: data¶
默认数据格式是 ndarray 负载类型的 data。input.data 文件看起来如下示例
[[1, 2, 3]]
[[4, 5, 6]]
[[7, 8, 9]]
[[1, 3, 6]]
输入文件中的每一行代表一个推理请求实例。 这些将被发送到模型如下
{"data": {"ndarray": [[1, 2, 3]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"batch_index": 0, "batch_id": ..., "batch_instance_id": ...}}}
{"data": {"ndarray": [[4, 5, 6]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"batch_index": 1, "batch_id": ..., "batch_instance_id": ...}}}
{"data": {"ndarray": [[7, 8, 9]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"batch_index": 2, "batch_id": ..., "batch_instance_id": ...}}}
{"data": {"ndarray": [[1, 3, 6]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"batch_index": 3, "batch_id": ..., "batch_instance_id": ...}}}
选择 tensor 负载类型会将有效结果发送到模型
{"data": {"tensor": {"shape": [1, 3], "values": [1, 2, 3]}}, "meta": ...}
{"data": {"tensor": {"shape": [1, 3], "values": [4, 5, 6]}}, "meta": ...}
{"data": {"tensor": {"shape": [1, 3], "values": [7, 8, 9]}}, "meta": ...}
{"data": {"tensor": {"shape": [1, 3], "values": [1, 3, 6]}}, "meta": ...}
数据类型: raw¶
如果数据类型被指定为 raw,那么输入文件中的每一行都将按原样发送到模型。
在这种情况下,负载类型设置将被忽略。
当不使用微批处理时,每一行将被理解为独立的 SeldonMessage 并按原样发送到模型,包括 meta.tags 信息。
如果使用微批处理,则每个「原始」输入必须代表 ndarray 或 tensor 有效负载类型,并且仅包含单个推理请求。 在这种情况下,用户提供的标签不会发送到模型。 然而,它们将被合并到响应中并写入输出文件。
Example raw input.data may look like this for example
{"data": {"names": ["a", "b", "c"], "ndarray": [[1, 2, 3]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"customer-id": 0}}}
{"data": {"names": ["a", "b", "c"], "ndarray": [[4, 5, 6]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"customer-id": 1}}}
{"data": {"names": ["a", "b", "c"], "ndarray": [[7, 8, 9]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"customer-id": 2}}}
{"data": {"names": ["a", "b", "c"], "ndarray": [[1, 3, 6]]}, "meta": {"tags": {"customer-id": 3}}}
查看 #3702 获取额外信息。